Managing a multigenerational workforce is like conducting an orchestra, blending the unique strengths of each generation to create a harmonious symphony of skills, experiences, and perspectives.
Each generation brings its own assets and contributions to the workplace. Baby Boomers, the trailblazers of society, embody values like hard work, loyalty, and career stability. Gen Xers possess a wealth of experience and a pragmatic approach that cuts through any challenge. Millennials, also known as Gen Y, are tech-savvy trendsetters who embrace change and harness the power of digital tools for seamless communication and collaboration. Finally, Gen Z’s innovation and technological fluency allows them to effortlessly navigate the digital landscape, infusing it with creativity, adaptability, and a pursuit of diversity, equity, and inclusion.
While uniting these groups creates a boundless potential for ideas and progress, generational differences may cause workplace clashes due to diverse work styles, communication preferences, and values. Organizations face the challenge of bridging gaps to cultivate a balanced and efficient environment. This article explores the unique work patterns and preferences of each age group and offers strategies to drive optimal productivity.
Pressed for time? Here’s a quick summary…
-
Flexibility and schedule autonomy are universally valued due to differing peak productivity hours.
-
Work environments that are flexible, digitally equipped, and wellness-focused cater to a multigenerational workforce.
-
Providing regular feedback, fostering a positive culture, and providing ample professional development opportunities boosts productivity and job satisfaction.
Understanding Generational Productivity & Work Styles
In an era of rapid technological advancement and widespread adoption of flexible work arrangements, organizations must understand and embrace generational differences in work styles and preferences, as highlighted in Adobe’s recent research. Empowering their diverse workforce can maximize employee productivity and enhance job satisfaction.
Millennials (1981-1996) & Gen Z (1997-2012)
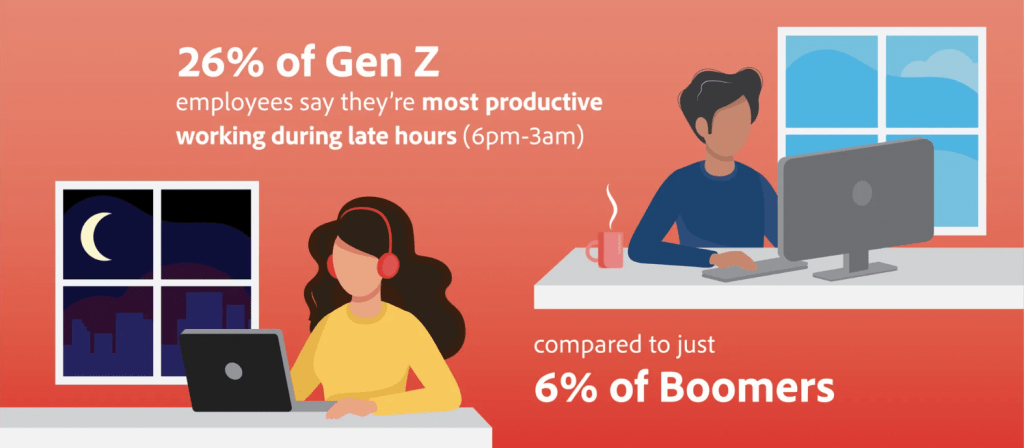
Over 60% of Millennial and Gen Z workers feel pressure to comply with traditional office hours despite being most productive outside those timeframes. Twenty-six percent of Gen Z and 18% of Millennials favor late hours (6pm to 3am) as their optimal window for productivity.
While they continue to conform to conventional work hours, younger employees seek out the most flexibility of any generation. About three-quarters indicate they’d leave their jobs for better work-life balance or more control over their schedule and two-thirds would switch for the option to work remotely.
Both Millennials and Gen Z place strong importance on digital fluency and efficiency. Seventy percent of Gen Z employees would change jobs for access to modern tools that can enhance their productivity.

Gen X (1965-1980)
Gen X upholds a more traditional approach toward work and productivity. They tend to appreciate direct communication, a focus on results, and career advancement opportunities. Gen Xer’s adaptability and resilience come from navigating economic and technological changes. Their inclination towards flexibility and remote work isn’t as pronounced as their younger counterparts, though it remains a desirable perk. Only 52% would consider changing jobs for superior tools, signifying caution toward digital tools compared to Millennials and Gen Z.
Boomers (1946-1964)
Boomers’ productivity patterns follow an early bird schedule, with more Boomers preferring the hours of 3am to 9am than any other generation. While Boomers are the least likely to feel obligated to stick to traditional office hours, their desire for flexibility, remote work, and digital tools doesn’t match the urgency demonstrated by younger generations. Only 37% would consider switching jobs for better productivity tools, and 50% for more flexibility.
Ways To Improve Productivity Across Generations
By implementing several strategies, organizations can create an environment where productivity remains at the forefront regardless of age or background.

1. Increase Flexibility
Flexibility and schedule autonomy are universally valued. Given the variances in peak productivity times and younger generations’ pursuit of improved work-life balance, organizations can embrace flexible work arrangements to cater to the needs of a multigenerational workforce. Popular arrangements include:
Offering flexibility promotes work-life harmony, reduces stress, prevents burnout, and enhances overall job satisfaction. It also significantly benefits those with caregiving responsibilities or other personal commitments, allowing them to adjust their schedules accordingly.
To maximize the efficiency of flexible work arrangements, organizations must prioritize results and quality of work over mere office presence. Conducting regular check-ins helps remote employees maintain a sense of belonging.
2. Prioritize Employee Well-Being
Wellness benefits aren’t just an employee perk – they’re a productivity tool. One study revealed a strong correlation between improved well-being and a productivity increase of up to 12%.
This highlights the strategic advantage of implementing a holistic wellness program that caters to the varying needs and preferences of different generations. Consider these examples of initiatives that address several dimensions of well-being and can resonate with each segment of a diverse workforce:
- Physical: A walking group can be inclusive to older employees who may prefer low-impact physical activity, while a kickboxing session may appeal more to younger workers who enjoy high-intensity exercise.
- Mental: Recognize the importance of mental health for all employees. Providing mindfulness/meditation training and workshops on resilience and maintaining work-life balance can be universally beneficial.
- Environmental: While environmental benefits like a carbon savings account may resonate more with younger generations, broader sustainability initiatives like starting a recycling program can unite all employees in contributing to a greener workplace.
3. Provide Feedback

The idea of feedback can inadvertently dampen employee morale if it’s mistaken for criticism. Reframing feedback as a constructive tool for growth can foster positivity and significantly boost productivity.
Effective feedback practices can vary across generations. Gen Z and Millennials often appreciate more direct and regular commentary, while Baby Boomers may prefer advice delivered more tactfully and indirectly. However, regardless of generational differences, consistency, openness, and two-way communication remain essential. The focus should be on identifying what’s working well and areas for improvement, encouraging employees and managers to collaboratively uplift performance and satisfaction.
Regular check-ins allow managers to promptly identify performance issues and offer consistent praise for employees’ strengths. Stay interviews are a powerful exercise as part of a broader framework for performance management. These interviews reverse the roles and put employers in the “hot seat”, allowing employees to speak candidly about their experiences at the company without fear of reprisal.
4. Foster A Positive Mindset & Culture
A thriving workplace culture is not merely a production hub; it’s a community where every team member feels recognized and valued. Demonstrating genuine care for employees’ well-being and career aspirations can counter apathy, fostering a supportive environment that enhances productivity.
The approach to cultivating a positive mindset can differ across generations. Recognition for years of service may resonate more with older generations, who value loyalty and commitment. Acknowledging their long-standing dedication to the organization through awards, ceremonies, or public appreciation can serve as a powerful motivator. Younger generations, who prioritize growth, continuous learning, and career advancement, often flourish through opportunities for professional development and mentorship. Offering them avenues to acquire new skills, attend workshops or conferences, and engage in mentoring relationships allows them to feel empowered and supported in their professional journeys. When individuals believe they are valued contributors to a larger purpose, they are naturally motivated to be more productive.
5. Offer Professional Development Opportunities

Professional development plays a pivotal role in employee retention and productivity. One survey exposed a lack of career development and advancement as the top reason for quitting a previous job. This underscores the imperative to provide employees with professional and personal growth opportunities.
A one-size-fits-all approach to development doesn’t suffice in a multigenerational workforce. Millennials and Gen Z may gravitate toward mentorship programs and tech-driven learning platforms for personalized guidance from experienced professionals. They embrace e-learning modules and online courses for flexible, self-paced learning. More seasoned workers, such as Baby Boomers and Gen X, favor traditional workshops, in-person training sessions, and leadership opportunities. They value face-to-face interactions and hands-on learning experiences to enhance their managerial skills.
By customizing opportunities to suit the needs and preferences of each generation, organizations include all employees in a culture of continuous learning. This not only amplifies employees’ skillsets, fueling productivity, but it also boosts job satisfaction, fostering a more engaged and fulfilled team.
6. Implement Efficient Digital Tools
The demand for efficient digital tools is especially pronounced among tech-savvy younger generations. However, with the rise of remote work and the rapid evolution of technology, the importance of leveraging artificial intelligence and other advanced tools is escalating across all age groups. Implementing these tools ramps up productivity and efficiency, keeping organizations ahead in an increasingly digital era, while also enhancing job satisfaction by simplifying complex work processes. The integration of technological advancements like AI may lead to a sense of ‘cultural shock’ for Baby Boomers, as it requires them to adapt to significant shifts in behaviors and mindset. Acknowledging the impact of these changes, fostering open communication, and establishing trust can create open-mindedness among hesitant employees.